Medical Communications is the communication of scientific, medical, pharmaceutical and biotechnology information and data to various audiences. It involves:
- Medical writing, the research, development and production of print or digital documents that deal specifically with medicine or health care.
- Editing, ensuring content is consistent, grammatically correct and in compliance with relevant guidelines.
- Payer/clinician engagement, conducting interviews to gain expertise or advice regarding disease management, HTA strategy, or other issues encountered in the health technology life cycle.
YHEC’s in-house Medical Communications team works both independently and cross functionally with all teams at YHEC.
Medical Communications services include:
- HTA dossiers: The Medical Communications team drafts the background and clinical sections of HTA dossiers and is responsible for compiling the complete HTA dossier with input from the RIS and HEM team.
- Publication planning and delivery: YHEC’s Medical Communications team uses a strategic approach and robust publication planning process to develop high-quality publications that meet peer-review requirements. This includes manuscripts, conference abstracts, posters, slide decks and other deliverables.
- Evidence dossiers: Reports that detail the disease background, unmet need and data gaps in a particular disease area. They are usually developed using pragmatic search strategies and can therefore be produced in a shorter time frame than SLRs.
- Global value dossiers: These detailed reports provide all the relevant information about a particular disease area and its treatments, including where the new technology will fit in the current care pathway. These documents are usually produced from a global perspective and can then be adapted for local HTA needs.
- Executive slide decks: YHEC’s Medical Communications team can provide an executive summary of any report in an easy-to-read slide deck, structured as a series of infographics.
- Care pathway analysis (including guideline review): The Medical Writing team has undertaken many guideline reviews, which can then be used to inform detailed care pathway analyses. Care pathway analysis (CPA) is a methodology that allows the identification of the medical decisions within the current pathway and within the new proposed pathway, where the new technology under investigation is embedded.
- Early payer interviews: In the pre-trial phase, early engagement with local payers and key opinion leaders can be useful to understand the potential challenges a new technology will face and develop strategies to overcome these. Early payer engagement may also be useful in developing value messaging, which shapes the narrative put forward in an HTA submission.
- Objection handlers and advisory boards:YHEC’s Medical Communications team can help you pressure test your value claims and work with you to prepare responses to key questions and challenges that affiliates may face.
YHEC’s Medical Communications team can provide support and editing for all types of documents, including SLR reports, pragmatic reviews, economic reports, digital media and conference abstracts/posters.
Medical Communications projects
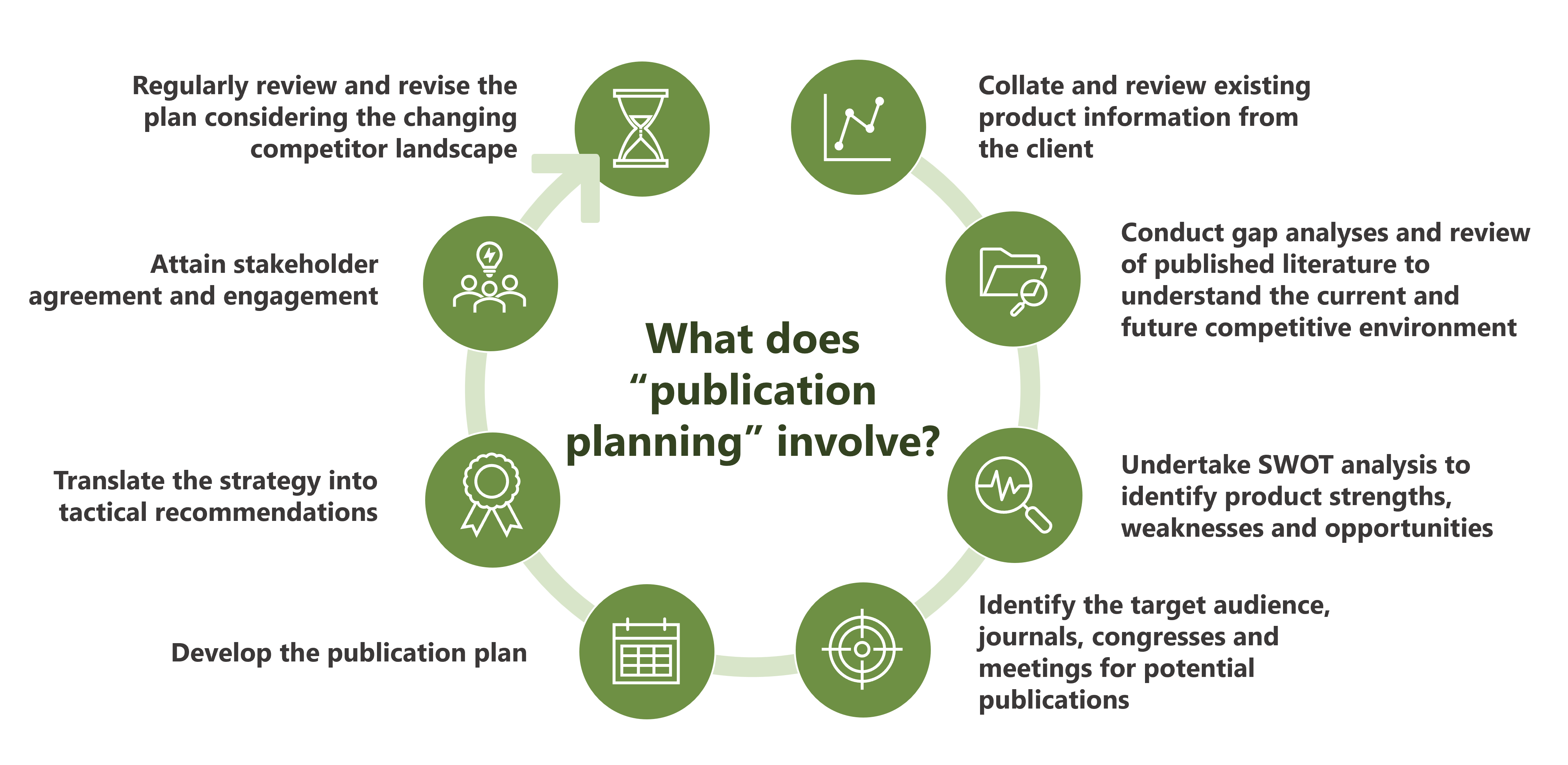
Publication planning
YHEC’s Medical Communications team can work with you to develop and execute a robust publication strategy to maximise impact and engagement with key stakeholders. The strategy will include consideration of a range of dissemination avenues including manuscripts, conference abstracts, presentations, posters and slide decks.
Discovery
Evidence dossiers:
Evidence dossiers provide an overview of a particular disease/indication and its treatments. Including the burden of illness and the associated HRQoL, the unmet need and cost-effectiveness of current treatments.
These types of documents are useful for gap identification and may inform where future technology development may be best targeted.
Early stage development
Care pathway analysis:
The care pathway is the journey a patient (or patients), with a certain medical condition, takes during an episode of healthcare.
These projects involve engagement with experts in the field to understand the differences in suggested care pathways and real-world practice.
Early value messaging:
YHEC can offer early value message development alongside care pathway analysis.
These messages ultimately form the value proposition which helps shape the narrative of the technology for HTA.
Early payer engagement:
Early payer engagement with HTA experts and clinicians can be useful to identify potential challenges the technology may face at HTA and find solutions to these.
Early engagement may also be used to inform appropriate trial endpoints.
Trial phase
Global value dossiers (GVDs):
GVDs provide an overview of all key elements of a new technology.
They are usually interlinked with the value proposition (core value messages). The topics in a GVD usually detail the research and data to support the value proposition.
GVDs can highlight data gaps and are often leveraged for HTA submissions.
Pre-launch
HTA dossiers:
YHEC’s in-house Medical Communications team can prepare full HTA submissions for NICE, the SMC and can also prepare AMCP dossiers for US submissions.
HTA submission
YHEC’s in-house Medical Communications team can provide writing and editorial support for post-HTA submission responses.
Medical Communications: Evidence dossiers
Evidence dossiers provide an overview of particular disease/indication and its treatments. Including:
- The pathophysiology of disease
- The burden of illness
- The current treatment
- Unmet need associated with treatment (treatment limitations)
- The cost-effectiveness of current treatments (based on published cost-effectiveness studies)
- The HRQoL associated with the disease and its treatment (based on published HRQoL studies)
- Alternatively, certain topics can be prioritised in evidence dossiers.
Evidence dossiers are often targeted to particular countries and are usually informed by pragmatic search methods. This means that an extensive overview of the disease area can be produced in less time than would be required for an SLR.
Evidence dossiers can be useful in highlighting gaps in current knowledge and pinpointing areas for future research. As such, it is advisable to work on evidence reviews early in the technology development pathway. Information from evidence dossiers can be used later in the technology cycle to inform the background sections of HTA submissions.
Medical Communications: Global value dossiers (GVDs)
GVDs provide an overview of all key elements of a new technology. They are usually interlinked with the value proposition (core value messages) but provide more detail on the evidence used to support the value proposition.
GVD topics usually include:
- The pathophysiology of disease
- The burden of illness
- The current treatment
- Unmet need associated with treatment limitations
- The cost-effectiveness of current treatments
- The HRQoL associated with the disease and its treatment
- The place for the new intervention in the treatment pathway*
- The safety and efficacy of the new intervention*
- The cost-effectiveness of the new intervention*
- The background sections of a GVD are usually informed by pragmatic search methods, meaning that an extensive overview of the disease area can be produced in less time than would be required for an SLR.
- SLRs can be incorporated into a GVD if the client wishes to commission this. In such cases, the medical writing and RIS team would collaborate on the GVD.
- It is advisable to work on GVDs early in the technology development pathway as the information gathered can be used to refine the core value story which forms the basis of HTA submissions
Medical Communications: Payer interviews
- Early payer interviews are appropriate for the early stages of clinical trial development and preliminary value messaging.
- Payer interviews may involve a detailed review of statistical analysis plans, early models and trial outcomes. They can help to inform the types of endpoints that should be assessed for a given indication.
- Payer interviews can also be useful to develop preliminary value messages for a new technology. These value messages ultimately form the narrative put forward in HTA submissions.
- The information arising from payer interviews can be shared either in a report or in an executive slide deck
 Local Health and Public Sector Organisations
Local Health and Public Sector Organisations